UCWriter
Import and Initialise
from amee_utils.writer import UCWriter
catalog_name = "heiaepgah01pwe01"
schema_name = "uc_writer_test"
uc_writer = UCWriter(
spark=spark,
catalog_name=catalog_name,
schema_name=schema_name
)
A Note on Partitioning
The write and overwrite functions of the writer allow for partitioning of the Delta Table through the partition_col kwarg:
Partitioning should be used when the expected data is intended to grow.
Example
catalog_name- The name of the catalog you want to write to.
An example could be
catalog_name='heiaepgah01pwe01'. schema_name- The name of the schema you want to create or update.
An example could be
schema_name='uc_writer_test'.
from amee_utils.writer import UCWriter
catalog_name = "heiaepgah01pwe01"
schema_name = "uc_writer_test"
uc_writer = UCWriter(
spark=spark,
catalog_name=catalog_name,
schema_name=schema_name
)
In this example, you would be initialising the UCWriter to perform actions on tables inside the uc_writer_test schema of the heiaepgah01pwe01 catalog.
UCWriter.write()
Without Unique Index
from pyspark.sql.types import StructType, StructField, StringType, IntegerType
# Define the schema for the DataFrame
df_schema = StructType([
StructField("name", StringType(), True),
StructField("age", IntegerType(), True)
])
# Create a sample DataFrame with random names and ages
data = [("John", 28), ("Alice", 24), ("Bob", 35), ("Eve", 40), ("Sam", 30)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, df_schema)
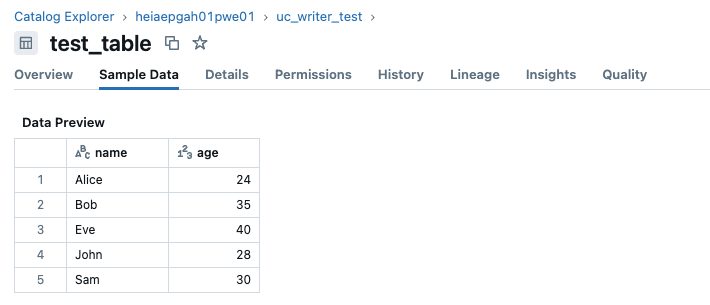
table_name = "test_table"
# Use write method to save the DataFrame
uc_writer.write(
df=df,
table_name=table_name,
)
Example
df- The PySpark DataFrame you want to save to a Unity Catalog table.
table_name-
The name of the table you want to create or update.
An example could be
table_name='test_table'.
from pyspark.sql.types import StructType, StructField, StringType, IntegerType
# Define the schema for the DataFrame
df_schema = StructType([
StructField("name", StringType(), True),
StructField("age", IntegerType(), True)
])
# Create a sample DataFrame with random names and ages
data = [("John", 28), ("Alice", 24), ("Bob", 35), ("Eve", 40), ("Sam", 30)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, df_schema)
table_name = "test_table"
# Use write method to save the DataFrame
uc_writer.write(
df=df,
table_name=table_name,
)
If the Unity Catalog table does not already exist, this will create a new table with the specified name in the schema and catalog defined during initialisation.
With Unique Index
# Create a sample DataFrame for testing
data = [("John", 28), ("Alice", 24), ("Bob", 35), ("Eve", 40), ("Sam", 30)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, df_schema)
# Use write method to save the DataFrame with a unique index
uc_writer.write(
df=df,
table_name="test_table_with_unique_index",
unique_index=True,
id_column_name="unique_id",
unique_identifiers=["name", "age"],
)
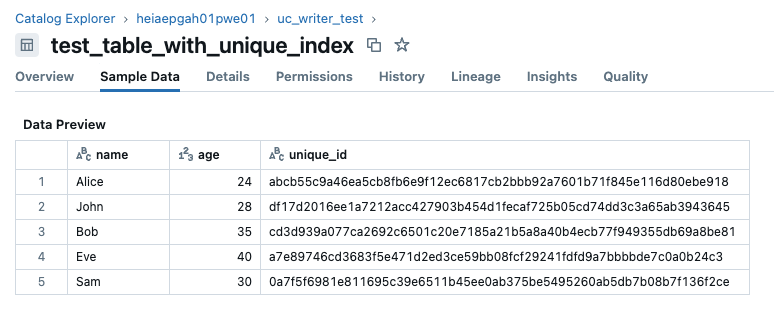
Example
df- The PySpark DataFrame you want to save to a Unity Catalog table.
table_name- The name of the table you want to create or update.
An example could be table_name='test_table_with_unique_index'.
unique_index- Bool [True]. This indicates that you would like the Unity Catalog table to contain a unique identifier column.
id_column_name- This is the name for your unique identifier column. An example could be
id_column_name="unique_id". unique_identifiers- This is a list of columns you would like to use to generate the unique value with. An example could be
unique_identifiers=["name", "age"]. This concatenates the values for each row in the"name"and"age"columns using the separator||, and then creates a unique hash for that row using sha256.
# Create a sample DataFrame for testing
data = [("John", 28), ("Alice", 24), ("Bob", 35), ("Eve", 40), ("Sam", 30)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, df_schema)
# Use write method to save the DataFrame with a unique index
uc_writer.write(
df=df,
table_name="test_table_with_unique_index",
unique_index=True,
id_column_name="unique_id",
unique_identifiers=["name", "age"],
)
If the Unity Catalog table does not already exist, this will create a new table with the specified name in the schema and catalog defined during initialisation. This table will now include a column named unique_id.
UCWriter.overwrite()
# Sample DataFrame for overwrite (completely new data)
overwrite_data = [("Lucy", 28), ("Mike", 38), ("Emma", 33)]
overwrite_df = spark.createDataFrame(overwrite_data, df_schema)
# Overwrite the existing table with new data
uc_writer.overwrite(
df=overwrite_df,
table_name=table_name
)
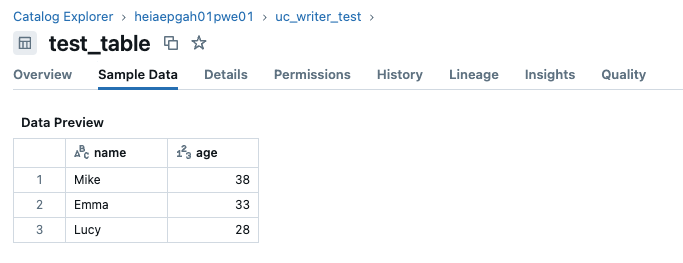
Example
overwrite_df- The new PySpark DataFrame you want to save to a Unity Catalog table. This will overwrite the existing data in that table.
table_name- The name of the table you want to overwrite.
An example could be table_name='test_table'.
From the first example, we wrote data to test_table. After using the overwrite() method, the data in the table will be completely replaced with the new data.
UCWriter.upsert()
# Sample DataFrame for upsert (some existing, some new)
upsert_data = [("John", 29), ("Alice", 24), ("Sam", 32), ("Tom", 40)]
upsert_df = spark.createDataFrame(upsert_data, df_schema)
# Upsert data into the table using the 'name' and 'age' combination as the unique identifier
uc_writer.upsert(
df=upsert_df,
table_name="test_table_with_unique_index",
id_column_name="unique_id",
unique_identifiers=["name", "age"]
)
Example
upsert_df- The new PySpark DataFrame you want to upsert to the Unity Catalog table. This will update the existing data in that table by inserting new rows or updating rows where the unique index matches.
table_name-
The name of the table you want to upsert data into.
An example could be
table_name='test_table_with_unique_index'. id_column_name- The name of the unique identifier column created when the table was written with a unique index.
unique_identifiers- The list of columns used to generate the unique value. This should match the columns used when creating the table with a unique index.
From the example where a Unity Catalog table was created with a unique index, we can then update that table and insert new data with the upsert() method.
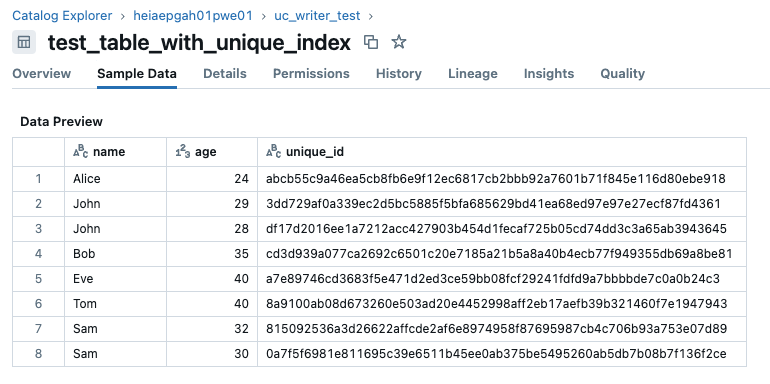
Note that the rows for John and Sam were updated with their new ages, the row for Alice remained unchanged, and a new row for Tom was inserted.